univariate_time_series_forecast
Tutorial and use case
Syntax
univariate_time_series_forecast(<table_name>, <time_column_name>,
<value_column_name>, <forecast_period>,
<period_unit>)
Arguments
<table_name> (string) - the data table's name.
<time_column_name> (string) - the name of a timestamp column in the data table.
<value_column_name> (string) - the name of a value column to be forecasted.
<forecast_period> (integer) - forecast period.
<period_unit> (string) - unit alias of the period.
Available <period_unit> aliases and descriptions:
| Alias string | Description |
|---|---|
| 'B' | business day |
| 'D' | calendar day |
| 'W' | week |
| 'M' | month |
| 'Q' | quarter |
| 'Y' | year |
Check out the Input data prerequisite for this here
Example
SQL statement
CALL univariate_time_series_forecast('SALES_TABLE', 'SALES_DATE', 'TOTAL_SALES', 24, 'M');
Description
Based on historical SALES_DATE and TOTAL_SALES data in SALES_TABLE, forecast the TOTAL_SALES value for the next 24 M (months).
Result
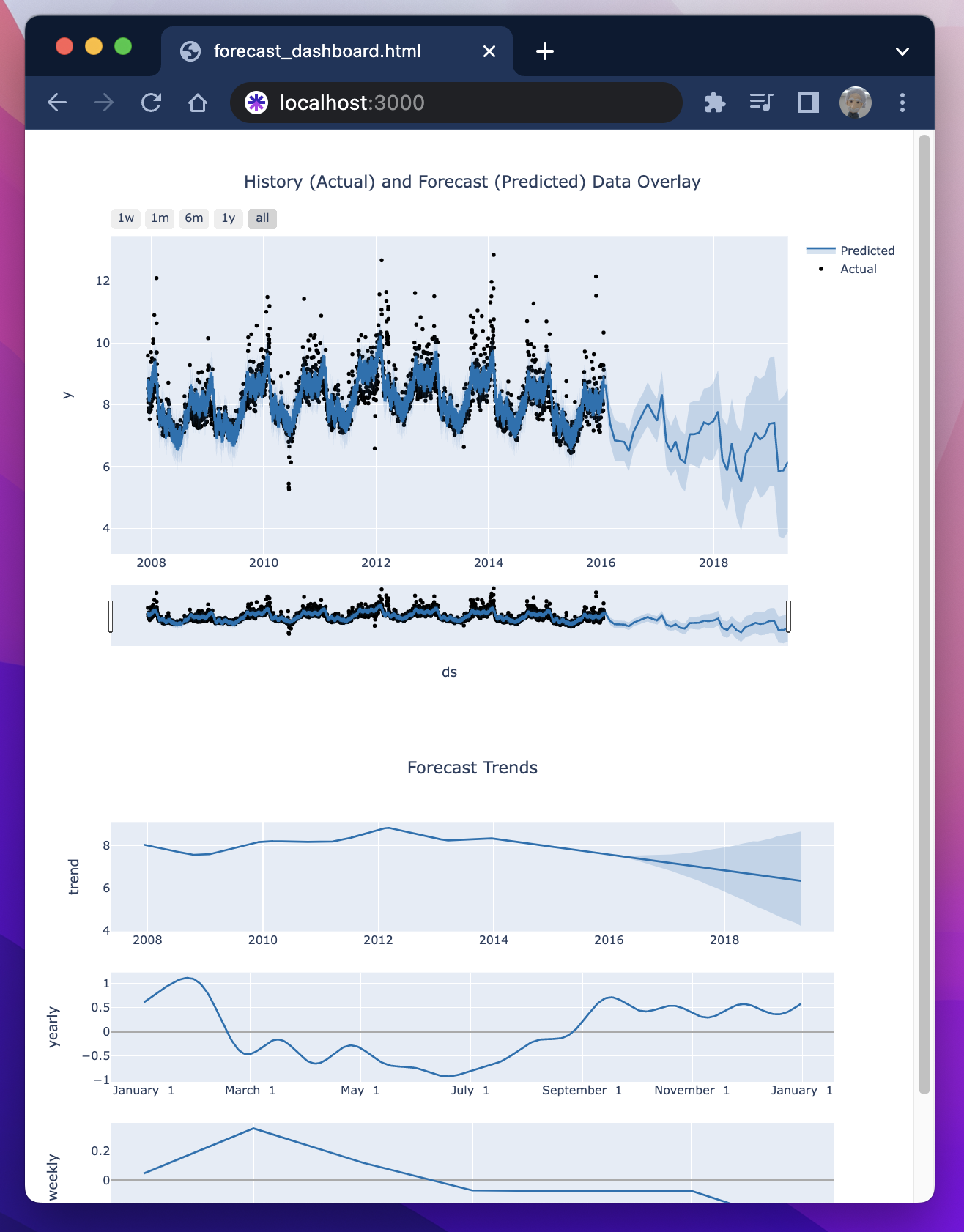
All historical and forecasted data is materialized as a new table.
A forecast dashboard is auto-generated for checking modeling accuracy, discovered trends, and predictions.
Prerequisite
Input data format
Input data is a univariate time series data: a sequence of integer or float data points indexed in timestamp. The table to be used should include in the following two columns:
- A Time stamp column. Data type:
Date & Time Data Types. - A value column. Data type:
Fixed-point NumberorFloating-point Number.
Extended reading. Snowflake docs about: Date & Time data types; Numeric data types.
Sample dataset: